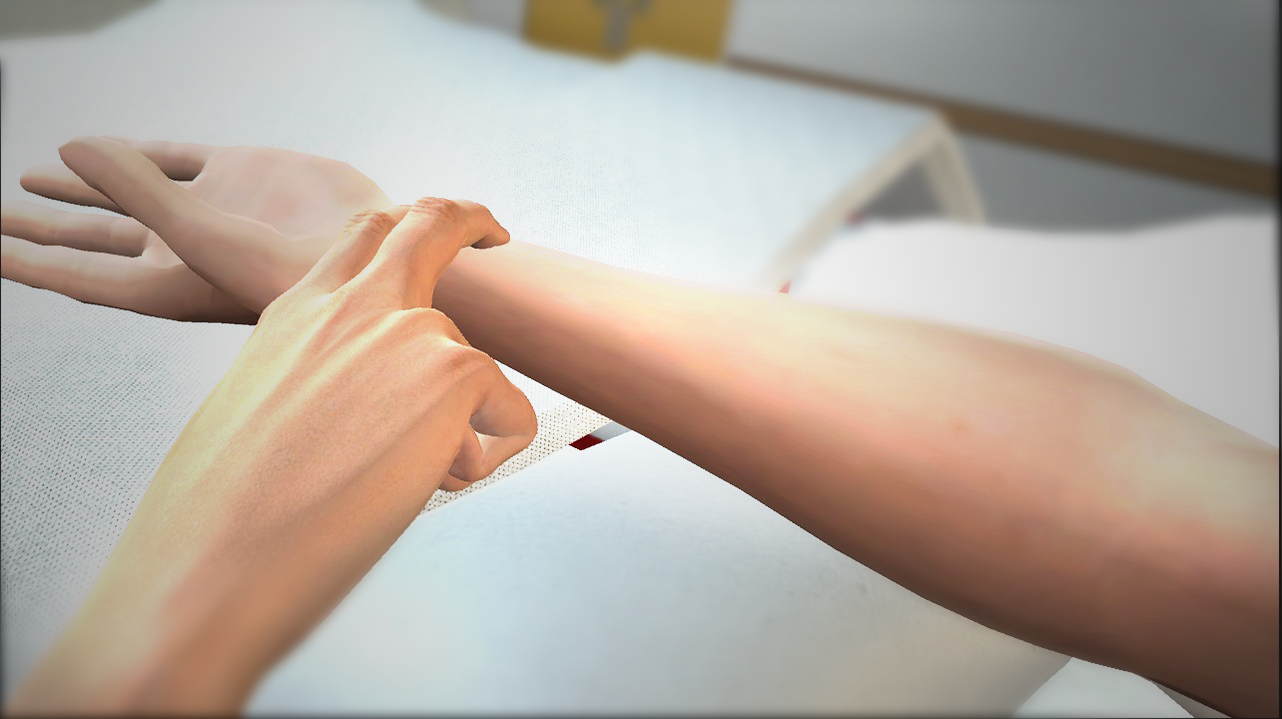
Measuring Radial Pulse and Respirations
Respirations and pulse rates are measured as part of the vital signs skill set.
Respirations: The process of respiration culminates in the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the lungs. This is achieved by the cardiovascular system and the respiratory system working together (Koutoukidis, Stainton & Hughson 2017). Assessment of respirations determines whether a person is receiving adequate oxygen or not. A nurse must use their sense of touch, sight and hearing to assess the rate, rhythm, depth and sound of a client’s respiration.
In a healthy adult, normal respirations should be within the range of 12–20 breaths per minute (Koutoukidis et al. 2017).
Pulse: Measurement of the pulse involves palpating an artery as it passes over a hard surface at specific sites around the body. The most commonly assessed pulse is the radial pulse, which is palpated in the wrist in alignment with the thumb. This observation is included when measuring a person’s vital signs. A nurse or healthcare provider must use their sense of touch to accurately count a pulse for 60 seconds—referred to as the pulse rate—and document this on the appropriate chart.
While counting the pulse rate, a nurse is also assessing the rhythm and volume of the pulse they are feeling. For example, the pulse may feel strong or weak, bounding or thready.
A normal pulse rate (Koutoukidis et al. 2017) in a healthy adult is between 60 and 100 bpm (beats per minute).