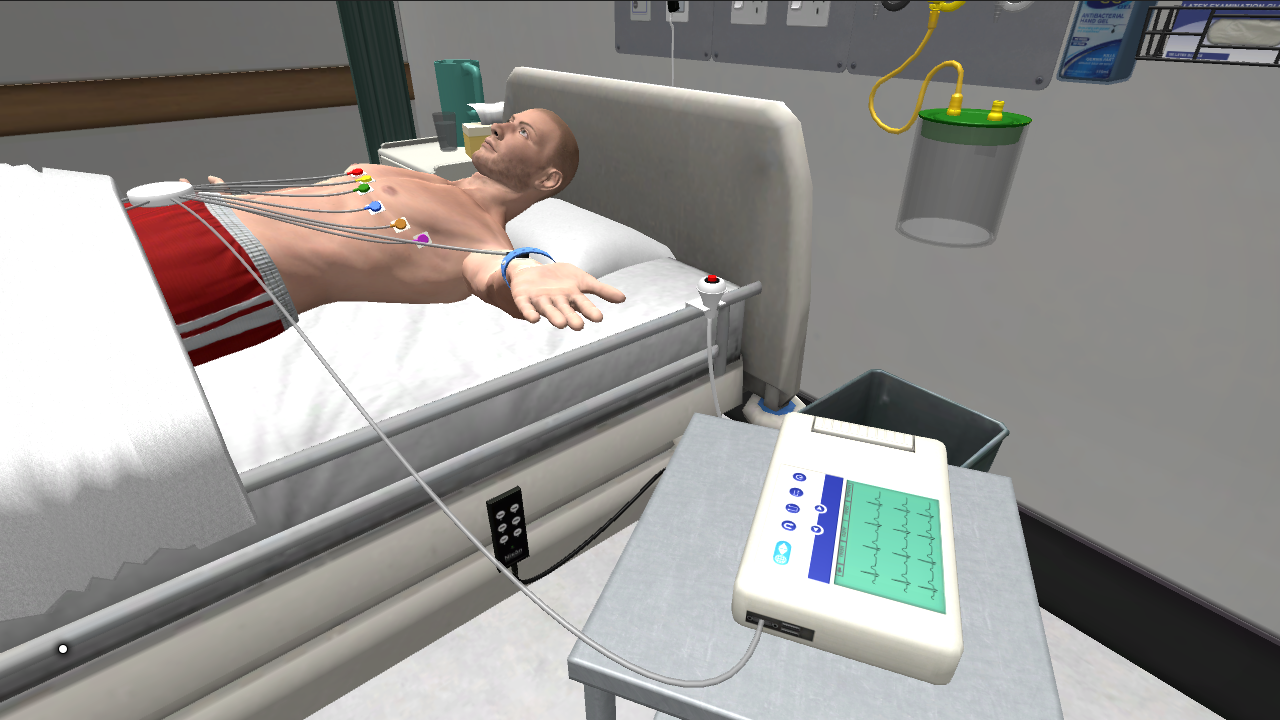
Perform an Electrocardiogram (ECG)
Electrocardiographs are used to check a heart’s electrical activity. It is a noninvasive procedure that can help to identify heart conditions in a client, such as a cardiac arrhythmia, poor blood flow or heart attack.
A 12 lead electrocardiogram (ECG) registers the electrical activity of the heart from 12 different viewpoints. The ECG machine records this electrical activity as waveforms, named P, Q, R, S, T waves, and transcribes these waveforms onto a monitor or tracing paper. The recording illustrates the rate, rhythm and regularity of the heart rate. It can also detect enlargement of the heart, decreased blood flow, inflammation of the pericardium and/or damage to the myocardium.
Indications for a client undergoing a 12 lead ECG include:
- identification of pathological conditions, for example chest pain, myocardial infarction and cardiac arrhythmia
- provision of a baseline ECG for comparison prior to other interventions or procedures, for example, surgery
- comparision of the present state of the heart’s electrical activity after a condition or illness has been identified.
The nurse performing the ECG needs to be familiar with the equipment and have a basic knowledge of ECG interpretation to identify life-threatening events.